|
TAO Project |
|
The TAO project

|
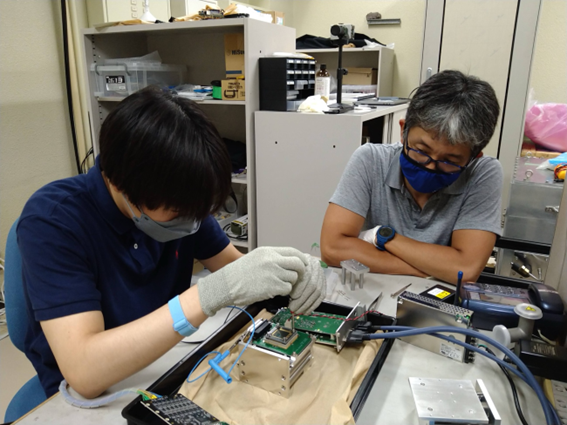
Development status of a near-infrared high-resolution spectrograph, TARdYSFor TAO Telescope, three first-generation instruments, MIMIZUKU, NICE, and SWIMS, which will be used from the first-light, have been developed. Currently, a new spectrograph TARdYS is being developed to follow them at Centro de Astro-Ingenieria de la Universidad Catolica (AIUC). TARdYS, standing for "AO AIUC high-Resolution(d) Y-band Spectrograph", is a spectrograph which has a high wavelength resolution (λ/Δλ>50,000) in the near-infrared Y-band (0.84-1.15μm). Utilizing its high wavelength resolution, we are planning to discover exoplanets orbiting around nearby stars by accurately measuring changes in their radial velocities from the Doppler effect. As the absorption of the Earth’s atmosphere in the infrared wavelength is very low at the TAO site, we plan to observe red stars (M-type stars) with masses less than half of that of the Sun, which shines bright in the infrared.
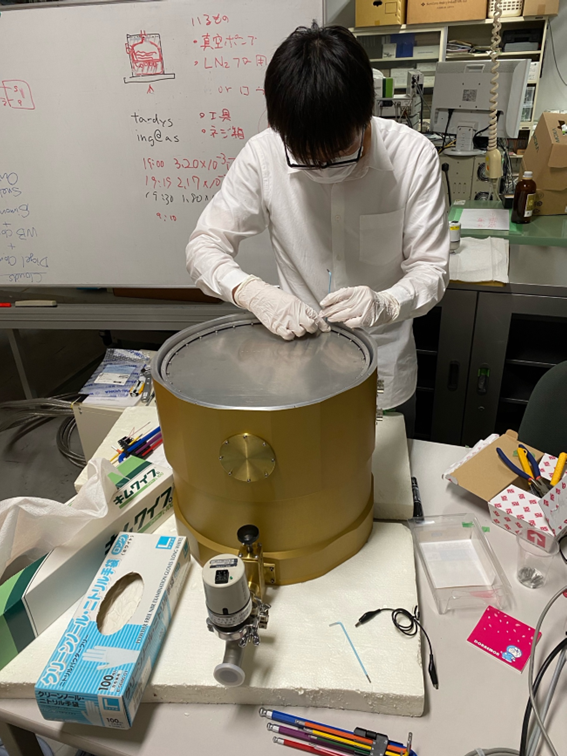
The team of Prof. Mamoru Doi and a graduate student Shogo Homan (at the time) at Institute of Astronomy, University of Tokyo, and Prof. Kentaro Motohara at NAOJ has developed a detector unit of TARdYS to acquire its spectral images in collaboration with AIUC. A large format InGaAs array sensor optimized to astronomical observations, developed by Hamamatsu Photonics and Associate Prof. Hidehiko Nakaya of NAOJ, was adopted for the focal-plane infrared detector. To achieve high sensitivity in the infrared, the sensor must be placed in a vacuum dewar and cooled down to minus 100 degrees Celsius or less, and a low-noise readout system is necessary. Mr. Homan lead the development of the readout system based on Messia VI (developed by Prof. Nakaya) under a supervision of Prof. Nakaya. Performance evaluation of the array sensor installed in the vacuum dewar was completed in 2023, and it was proved to have sufficient performance to carry out observations mentioned above. The detector unit including the vacuum dewar will be transported to AIUC, Chile in the second half of 2024, and a full-scale test as a spectrograph will start after assembly with the optics of the spectrograph which is under production there.
Copyright(c) 2024 TAO Project, Institute of Astronomy, Graduate School of Science, University of Tokyo
|