miniTAO Full-Remote Operation Started
miniTAO has many difficulties on its operation because of its high altitude
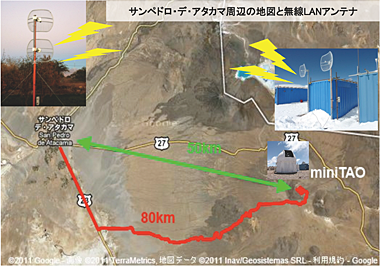
environment (5640 m) and long distance from the base camp at San Pedro de
Atacama (about 80 km).
The round-trip drive between the base camp and the summit observatory takes
about 4 hours. There are many dangers like snow coverage, rock fall, and harsh
weather along the way. The oxygen concentration on the summit is only about a
half of the normal living place. Cosmic-ray exposure is also one risk at the
summit. The operations and observations in such environment sometimes threaten
our lives. Then, for safe and efficient observations, wireless network has been
established between the base and the summit for remote operation. It connects
the way of about 50 km (linear distance) with radio as shown in figure below.
|
Nowadays, remote observing systems are often used among the world observatories
like the Subaru telescope in Hawaii and the ASTE telescope in Atacama in Chile.
Ahead of these observatories, the University of Tokyo had been operated the
MAGUNUM telescope at the summit of Haleakala in Hawaii from Japan totally
remotely.

|
▲Dome of MAGNAUM telescope at the summit of Haleakala in Hawaii.
It had been operated from Dec. 2000 to Dec. 2008.
|
Some equipment is required for remote observing system. In the miniTAO remote
observing system, highly accurate, stable and reliable network system was
constructed based on the experiment of the MAGNUM telescope.
At first, two pairs of the parabola antennae connecting the summit and the base
(a total of four antennae) were built at both places. One pair is prepared for
the backup line used when the main line is in trouble.
At first, two pairs of the parabola antennae connecting the summit and the base
(a total of four antennae) were built at both places. One pair is prepared for
the backup line used when the main line is in trouble.
There are also some systems for handling the emergency, like (1) a function
which close the dome slit in sensing the disconnection between the base and
summit, (2) a system against power failure which automatically shuts down the
machines at the summit by the exhaustion of batteries, (3) an alerting system
which judges and informs us of bad conditions for the telescope, like strong
wind and high humidity.

|
|
▲Various systems supporting remote observations.
|
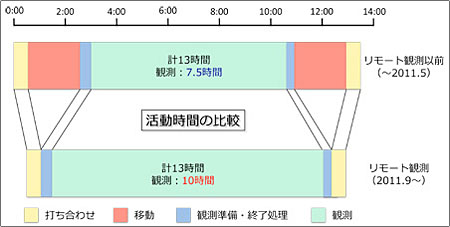
As mentioned above, there was a loss of observing time attributed to the dead
time of about four hours trip between the summit and the base. However, by this
establishment of remote observing system, observing efficiency will be much
improved because the dead time become utilized as the observing time.
|
▼Operating time table before and after completion of remote observing system.
|
|
※Typical case is shown here.Actual observing time varies depending on starting
and finishing of twilight.
※Mid-infrared observations are sometimes conducted in daytime. |
In this campaign, 15 ANIR programs of 156 hours and 8 MAX38 programs of 153
hours have been conducted. The total observing time increased about 20% compared
with the previous campaigns. In addition, MAX38 observing time especially
increased because the remote observing system enables us to utilize the daytime
observable time. (*In actual operation, it is sometimes required to go to the
summit for emergency response to the troubles of the telescope, dome, and power
failure or requirement of on-the-spot observations.)
Highly sensitive observations or utilizing new atmospheric windows require the
site with better condition (often harsh environment for observers). Ultimate
site is satellite telescopes. However, there are many difficulties like
expensive launch cost, limited observing time, long development time,
maintenance difficulty, etc. Taking into account these matters, ground-based
observatories will not disappear. It is likely that the mutual cooperation of
ground-based observatories and space observatories will bring fruitful results.
For such successful achievements, remote observing technics of ground-based
observatories will be much more important and necessary.
|





